For most Azure resources, Commvault provides a custom role that includes the permissions that are required to protect the resources. In non-production environments, you can use Azure built-in roles instead. For VMs encrypted with Azure Key Vault, you can use a custom role or an access policy, but access policies are less secure and are considered by Microsoft to be a legacy authorization system.
If there is no custom role for an Azure resource that you want to protect, you can create your own custom role.
For instructions to assign roles, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal.
Custom Roles
Important
In the JSON file, change placeholder values such as {subscription-id}.
|
Azure resources |
Custom role for Azure Portal |
Custom role for Azure CLI |
|---|---|---|
|
||
|
Azure VMs |
||
|
None |
|
|
Azure File Storage |
None |
Built-In Roles
| Azure resources | Assign to the subscription | Assign to the storage account |
|---|---|---|
|
|
None |
|
|
None |
| Azure VMs, encrypted |
|
None |
| Azure VMs, unencrypted |
|
None |
|
|
None |
| Azure File Storage | Storage Account Contributor |
|
Permissions for Confidential VMs Encrypted with Azure Key Vault Using RBAC
To restore confidential VMs that are encrypted using Azure Key Vault with RBAC, assign the following roles:
| Azure resources | Assign to the Confidential VM Orchestrator built-in app | Assign to your Azure application |
|---|---|---|
| Confidential VMs, encrypted using Azure Key Vault with RBAC | Key Vault Crypto Service Release User | Key Vault Data Access Administrator |
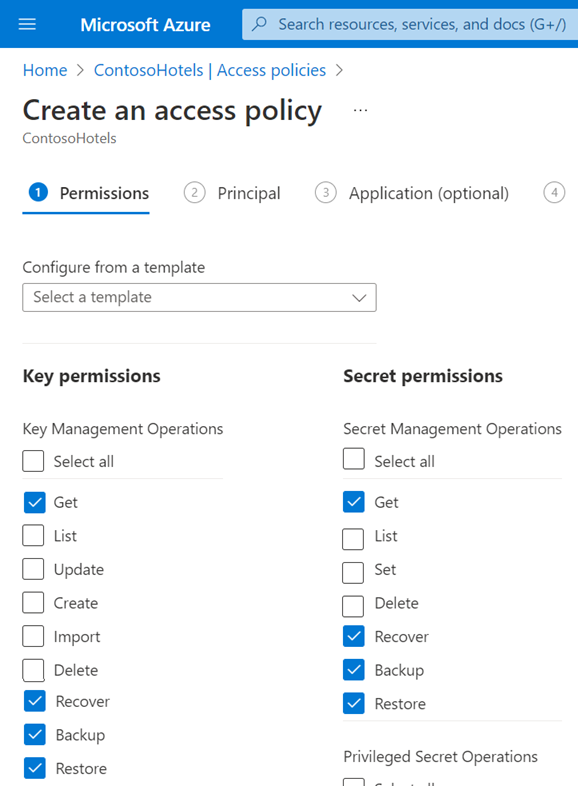
Permissions for VMs Encrypted with Azure Key Vault Using Access Policies (Legacy Authorization System)
For Azure VMs that are encrypted with Key Vault, instead of using a custom role that you assign to your Azure Key Vault application, you can create an access policy and assign it to the Azure VM or the Azure Key Vault application that functions as your service principal.
For instructions to create an access policy in the Azure portal, see Assign a Key Vault access policy (legacy).
| Azure resources | Permissions to select for both Key permissions and Secret permissions |
|---|---|
| VMs, encrypted using Azure Key Vault with access policies |
|
Note
The Commvault Cloud software does not support VMs that are encrypted with Azure Key Vault for managing certificates.